近年来,随着人工智能(artificial intelligence,AI)技术的飞速进步,特别是机器学习和深度学习技术在医学领域的广泛应用,我们正迈向医疗健康领域的新时代[5-6]。AI技术通过高效处理和分析海量医疗数据,揭示了疾病复杂的生物学机制,快速推动了临床决策过程,为患者提供了更加个性化和精确的医疗服务[7⇓-9]。具体而言,在子宫内膜癌的早期筛查、精确诊断、个性化治疗方案的设计、治疗效果评估以及疾病预后分析等方面,AI技术展现出了巨大潜力。例如,通过对患者的基因表达数据、影像学资料和病理样本进行分析,AI能够精准识别肿瘤的特征,预测疾病的进展和治疗效果,为临床医生提供了有力的决策支持[10]。此外,AI技术还能够协助医生更准确地进行风险评估和制定个性化治疗计划,显著提高治疗效果并减少不必要的医疗干预[11]。尽管AI在子宫内膜癌诊疗中展现出巨大潜力,但其应用仍处于初级阶段,面临着诸多挑战,如数据质量和可用性、算法的可解释性以及伦理法律问题等。因此,对AI技术在该领域的研究进展和潜在影响进行深入分析和探讨,对于推动其在临床实践中的广泛应用并克服当前挑战具有重要意义。
本综述旨在综合分析AI技术在子宫内膜癌筛查、诊断和治疗决策支持中的最新研究进展,探讨其面临的挑战及未来的发展方向,以及为医疗专业人员、研究学者及相关政策制定者提供有价值的参考信息,进一步促进AI技术在提高子宫内膜癌患者诊治效率和效果中的应用。
1 AI在子宫内膜癌筛查和诊断中的应用
随着AI技术尤其是机器学习和深度学习的迅速发展,其在医学影像分析、病理学研究和生物信息学等领域的应用逐渐成熟,为子宫内膜癌的早期发现和精确诊断提供了新的可能性[12]。
1.1 医学影像分析
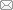
在医学成像领域,主要尝试将AI引入超声、MRI和CT,利用深度学习等AI技术,可以建立自动化的影像识别系统,有效提升诊断的准确性和效率。Zhang等[17]研究了基于卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network,CNN)构建子宫内膜癌预测的成像模型,并结合临床信息建立了综合预测模型智能识别预测子宫内膜癌,训练组影像组学模型和综合预测模型的受试者工作特征曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)分别为0.897和0.913,试验组影像组学模型和综合预测模型的AUC分别为0.889和0.897,证实了影像组学参数可作为无创标志物预测子宫内膜癌的有效性。Coada等[18]采用CT对81例子宫内膜癌患者进行影像学特征提取,并用最小绝对收缩和选择算子-Cox比例风险(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator-Cox proportional hazards,LASSO-Cox)、似然增强Cox比例风险(Cox proportional hazards model with boosting,CoxBoost)、随机森林(random forest,RF)3种机器学习模型来预测患者的无病生存期(disease free survival,DFS),结果表明所有模型中,被机器学习模型归类为具有高复发风险预测的患者表现出更差的DSF(P<0.001),证明了影像学在预测子宫内膜癌复发方面的潜力。基于MRI的AI子宫内膜癌诊疗模型能够自动识别和量化影像资料中的特征,包括肿瘤的形状、边缘以及与正常组织的界限,甚至能够发现人眼难以察觉的细微变化[19]。另有研究基于从CT图像中手动分割的病变提取的放射组学特征来预测子宫内膜癌的阶段(见图1)[20]。这些研究已经证明,AI辅助的影像诊断在识别特定类型的肿瘤、预测病变性质方面达到了与资深放射科医师相当乃至更高的准确率[21]。
图1
1.2 病理组织图像分析
病理诊断是子宫内膜癌诊断的“金标准”。AI在病理图像分析领域的应用,特别是深度学习算法在组织学图像分析中的应用,为提高病理诊断的准确性和效率开辟了新路径。这些技术能够自动识别病理切片中的癌细胞、评估肿瘤的分级和侵袭性、识别肿瘤微环境中的免疫细胞分布等复杂特征[22]。
1.3 基因数据分析
AI技术不仅可以帮助研究人员在复杂的基因数据中识别出有助于预测病情和治疗反应的遗传标志,而且可以通过综合分析基因数据、临床特征和环境因素等多维度信息,构建更为准确的疾病预测模型[29]。这些模型有望在精准医疗领域发挥重要作用,为子宫内膜癌患者提供个性化的治疗建议。
综上所述,AI技术在子宫内膜癌的筛查和诊断中显示出了巨大的潜力。通过对医学影像、病理组织以及基因数据的深入分析,AI不仅能提高诊断的准确性和效率,还能为临床决策提供有力的支持。然而,在普及这些技术之前,我们还需要克服数据质量、模型解释性以及临床集成等一系列挑战,以确保这些技术能够安全、有效地服务于患者。
2 AI在子宫内膜癌治疗决策支持与预后评估中的应用
随着对子宫内膜癌的深入研究以及治疗方法的不断进步,选择适合每位患者的治疗方案依旧是一个复杂挑战。AI技术的运用不仅为实现高度个性化的治疗决策提供了可能性,还为疾病的预后评估开辟了新路径。
2.1 个性化治疗方案的制定
在传统的治疗决策过程中,医生通常会根据患者的疾病分期、生物标志物、全身状态以及其他临床参数来设计治疗方案。然而,这种方法往往忽视了患者间的微妙差异,以及肿瘤生物学特性的复杂性。借助机器学习等AI技术,可以分析包括遗传信息、病理学特征、治疗历史以及患者个体偏好在内的多维度数据,为患者制定更为精确的个性化治疗方案[30]。
2.2 治疗效果评估与疾病预后分析
通过结合临床观察数据、实验室指标、影像学和病理学特征等多源数据,AI模型可以实时监测治疗反应,及时发现疾病进展或复发的迹象。此外,AI还能够分析大量患者数据,识别影响疾病预后的关键因素,从而预测个体患者的长期生存率和生活质量。这种基于数据驱动的预后评估不仅可以指导医生精准地调整治疗,而且能够为患者提供更为准确的预后信息,帮助他们做出更加明智的治疗和生活决策。
3 AI在子宫内膜癌研究领域的新动向
子宫内膜癌作为一种广泛影响女性健康的妇科恶性肿瘤,其诊断和治疗的复杂性要求高精度和个性化的医疗方法。随着AI技术,特别是机器学习和深度学习的进步,这一领域正经历着前所未有的技术革新。AI能在多模态数据融合分析、患者实时监控管理等方面促进子宫内膜癌的诊治和管理。
3.1 多模态数据融合与分析
多模态数据包含了临床检查、影像诊断结果、组织病理分析以及分子生物学特征等各个层面的信息。传统上,这些数据类型往往独立分析,而AI的应用促使数据融合成为可能,深度学习算法如CNN、循环神经网络(recurrent neural network,RNN)和图神经网络(graph neural network,GNN)等已被用于解决这一挑战[35]。
深度学习模型能够从放射影像识别出微妙的模式变化,这些模式可能在早期阶段反映疾病的存在,而裸眼观察难以捕捉。同时,将这些影像数据与病理学和分子遗传学数据相结合,可以进一步揭示疾病亚型和相关的生物标志物[36]。比如,AI算法可以通过分析肿瘤相关基因的表达模式,辅助医生在诊断过程中区分恶性程度和疾病预后,为精准治疗提供支持。
3.2 患者实时监控与管理
4 AI挑战与限制
虽然AI在子宫内膜癌诊治领域取得显著进展,但其广泛应用仍面临一系列挑战与限制。这些挑战既涉及技术层面的困难,也包括伦理、法律和数据质量的问题。在实现全面普及之前,必须对这些障碍进行细致考量并寻求有效的解决方案。
4.1 数据质量与可用性问题
来自不同医疗机构的数据往往因采集标准、设备类型和操作程序不一而缺乏一致性。此外,病理报告、医学影像等资料的格式差异,加之缺少统一的数据标注规范,严重影响了数据的兼容性和AI模型的训练质量。患者数据的敏感性要求高度的隐私保护和数据安全措施,但在现实操作中可能遭遇数据泄露和滥用的风险。确保数据安全的同时兼顾研究与治疗的需求,是当前面临的一大挑战。
4.2 模型泛化能力与解释性问题
尽管AI模型在特定数据集上的表现可能显示出卓越的性能,但其在不同人群、机构或地区中的泛化能力仍存在质疑。不同区域和人群的遗传背景、生活方式和环境因素等差异,都可能导致模型性能的波动。AI模型,特别是深度学习模型的“黑盒”特性,使其决策过程缺乏透明度和可解释性。这不仅为临床决策提出了难题,也可能在医疗责任归属、患者信任等方面制造障碍。
4.3 法律法规与伦理挑战
目前关于医疗AI的法律法规尚处于发展阶段,不同国家和地区的规定差异大,对AI技术的评估和认证流程缺乏统一标准。这使得跨国合作、产品的市场准入及商业化推广面临复杂的法律环境。
AI在医疗决策中的作用日益增强,引发了包括数据隐私、机器与人的责任界限、患者自主权等一系列伦理问题。如何确保技术发展符合伦理原则,维护患者利益,是必须认真对待的议题。
综上,在面对这些挑战时,需要医疗界、技术界与法律界等多方面专家的共同合作,通过建立严格的数据管理制度、改善算法的通用性和可解释性、形成科学合理的法规制度,以及培养医疗AI伦理观念,共同推进AI在子宫内膜癌领域的健康、有序和有效应用。此外,公众的教育和培训也极为关键。患者和医疗服务提供者需要对AI技术有充分的了解,以便正确评估和利用AI在提高治疗效果、降低医疗成本以及促进医疗公平性方面的潜力。此过程中,不断积累的实践经验和案例研究,将为解决现实问题提供宝贵的数据支持和启示。
5 结语与展望
近年来,AI在子宫内膜癌领域取得了显著进展,在早期诊断和预后评估方面展示出高效和精准的潜力。通过深度学习和机器学习算法,研究人员和临床医生能够从大规模医学影像和基因数据中提取有价值的信息,极大地促进了对子宫内膜癌病理机制的理解和个性化治疗策略的发展。AI技术在诊断中实现了高敏感度和高特异度,通过自动化分析医学影像和病理切片,帮助医生快速识别癌变组织,减少漏诊和误诊的发生。此外,AI在治疗方案选择和效果预测方面,通过分析患者的临床数据和基因信息,提供个性化治疗方案,提高治疗效果,降低不良反应的可能性。
未来AI在子宫内膜癌领域的应用将进一步深化。随着算法优化和计算能力的提升,AI将更加高效和精准地处理复杂医疗数据,实现精准化的预测模型。跨学科合作将推动AI与基因组学、免疫学等领域的结合,为早期筛查、靶向治疗和疫苗研发提供有力支持。长期来看,AI不仅将革新子宫内膜癌的诊断和治疗模式,还将推动医疗行业向高效、精准和个性化方向发展,实现医疗资源的优化配置。然而,这也带来了数据隐私、医疗伦理和法律监管的新挑战,需要通过持续的技术创新和政策制定来应对,确保AI技术的健康、有序应用,最终惠及每一位患者。
参考文献
Endometrial cancer
[J].Endometrial cancer is the most common gynaecological cancer in high income countries and its incidence is rising globally. Although an ageing population and fewer benign hysterectomies have contributed to this trend, the growing prevalence of obesity is the major underlying cause. Obesity poses challenges for diagnosis and treatment and more research is needed to offer primary prevention to high-risk women and to optimise endometrial cancer survivorship. Early presentation with postmenopausal bleeding ensures most endometrial cancers are cured by hysterectomy but those with advanced disease have a poor prognosis. Minimally invasive surgical staging and sentinel-lymph-node biopsy provides a low morbidity alternative to historical surgical management without compromising oncological outcomes. Adjuvant radiotherapy reduces loco-regional recurrence in intermediate-risk and high-risk cases. Advances in our understanding of the molecular biology of endometrial cancer have paved the way for targeted chemotherapeutic strategies, and clinical trials will establish their benefit in adjuvant, advanced, and recurrent disease settings in the coming years.Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Cancer of the corpus uteri
[J].
FIGO staging of endometrial cancer: 2023
[J].
Incidence, risk factors, and a prognostic nomogram for distant metastasis in endometrial cancer: A SEER-based study
[J].
Artificial Intelligence in Molecular Medicine
[J].
Introduction to Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning
[J].
Artificial intelligence in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis: Current application and future perspective
[J].Lung cancer is one of the malignant tumors with the highest incidence and mortality in the world. The overall five-year survival rate of lung cancer is relatively lower than many leading cancers. Early diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer are essential to improve the patient's survival rate. With artificial intelligence (AI) approaches widely applied in lung cancer, early diagnosis and prediction have achieved excellent performance in recent years. This review summarizes various types of AI algorithm applications in lung cancer, including natural language processing (NLP), machine learning and deep learning, and reinforcement learning. In addition, we provides evidence regarding the application of AI in lung cancer diagnostic and clinical prognosis. This review aims to elucidate the value of AI in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis as the novel screening decision-making for the precise treatment of lung cancer patients.Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Artificial Intelligence in Cardiology
[J].Artificial intelligence and machine learning are poised to influence nearly every aspect of the human condition, and cardiology is not an exception to this trend. This paper provides a guide for clinicians on relevant aspects of artificial intelligence and machine learning, reviews selected applications of these methods in cardiology to date, and identifies how cardiovascular medicine could incorporate artificial intelligence in the future. In particular, the paper first reviews predictive modeling concepts relevant to cardiology such as feature selection and frequent pitfalls such as improper dichotomization. Second, it discusses common algorithms used in supervised learning and reviews selected applications in cardiology and related disciplines. Third, it describes the advent of deep learning and related methods collectively called unsupervised learning, provides contextual examples both in general medicine and in cardiovascular medicine, and then explains how these methods could be applied to enable precision cardiology and improve patient outcomes.Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Emerging role of deep learning-based artificial intelligence in tumor pathology
[J].
High-performance medicine: the convergence of human and artificial intelligence
[J].The use of artificial intelligence, and the deep-learning subtype in particular, has been enabled by the use of labeled big data, along with markedly enhanced computing power and cloud storage, across all sectors. In medicine, this is beginning to have an impact at three levels: for clinicians, predominantly via rapid, accurate image interpretation; for health systems, by improving workflow and the potential for reducing medical errors; and for patients, by enabling them to process their own data to promote health. The current limitations, including bias, privacy and security, and lack of transparency, along with the future directions of these applications will be discussed in this article. Over time, marked improvements in accuracy, productivity, and workflow will likely be actualized, but whether that will be used to improve the patient-doctor relationship or facilitate its erosion remains to be seen.
The impact of artificial intelligence in medicine on the future role of the physician
[J].
The application of machine learning for predicting recurrence in patients with early-stage endometrial cancer: a pilot study
[J].
Editorial: Molecular pathology and computational image analyses in gynecologic malignancies
[J].
Impact of computed tomography-determined sarcopenia and artificial intelligence-driven waist skeletal muscle volume on survival outcome in endometrial cancer
[J].
Current Status of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Malignant Uterine Neoplasms: A Review
[J].
Using Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Network Approach to Identify the Invasion Depth of Endometrial Cancer in Myometrium Using MR Images: A Pilot Study
[J].
Deep Learning for Intelligent Recognition and Prediction of Endometrial Cancer
[J].
A Radiomic-Based Machine Learning Model Predicts Endometrial Cancer Recurrence Using Preoperative CT Radiomic Features: A Pilot Study
[J].
Artificial Intelligence and Radiomics for Endometrial Cancer MRI: Exploring the Whats, Whys and Hows
[J].
A systematic review on the use of artificial intelligence in gynecologic imaging-Background, state of the art, and future directions
[J].Machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) are terms that have made their way into nearly all areas of medicine. In the case of medical imaging, these methods have become the state of the art in nearly all areas from image reconstruction to image processing and automated analysis. In contrast to other areas, such as brain and breast imaging, the impacts of AI have not been as strongly felt in gynecologic imaging. In this review article, we: (i) provide a background of clinically relevant AI concepts, (ii) describe methods and approaches in computer vision, and (iii) highlight prior work related to image classification tasks utilizing AI approaches in gynecologic imaging.A comprehensive search of several databases from each database's inception to March 18th, 2021, English language, was conducted. The databases included Ovid MEDLINE(R) and Epub Ahead of Print, In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, and Daily, Ovid EMBASE, Ovid Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Ovid Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and ClinicalTrials.gov.We performed an extensive literature review with 61 articles curated by three reviewers and subsequent sorting by specialists using specific inclusion and exclusion criteria.We summarize the literature grouped by each of the three most common gynecologic malignancies: endometrial, cervical, and ovarian. For each, a brief introduction encapsulating the AI methods, imaging modalities, and clinical parameters in the selected articles is presented. We conclude with a discussion of current developments, trends and limitations, and suggest directions for future study.This review article should prove useful for collaborative teams performing research studies targeted at the incorporation of radiological imaging and AI methods into gynecological clinical practice.Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The efficacy of deep learning models in the diagnosis of endometrial cancer using MRI: a comparison with radiologists
[J].To compare the diagnostic performance of deep learning models using convolutional neural networks (CNN) with that of radiologists in diagnosing endometrial cancer and to verify suitable imaging conditions.This retrospective study included patients with endometrial cancer or non-cancerous lesions who underwent MRI between 2015 and 2020. In Experiment 1, single and combined image sets of several sequences from 204 patients with cancer and 184 patients with non-cancerous lesions were used to train CNNs. Subsequently, testing was performed using 97 images from 51 patients with cancer and 46 patients with non-cancerous lesions. The test image sets were independently interpreted by three blinded radiologists. Experiment 2 investigated whether the addition of different types of images for training using the single image sets improved the diagnostic performance of CNNs.The AUC of the CNNs pertaining to the single and combined image sets were 0.88-0.95 and 0.87-0.93, respectively, indicating non-inferior diagnostic performance than the radiologists. The AUC of the CNNs trained with the addition of other types of single images to the single image sets was 0.88-0.95.CNNs demonstrated high diagnostic performance for the diagnosis of endometrial cancer using MRI. Although there were no significant differences, adding other types of images improved the diagnostic performance for some single image sets.© 2022. The Author(s).
Artificial Intelligence for Predicting Microsatellite Instability Based on Tumor Histomorphology: A Systematic Review
[J].
Artificial intelligence for prediction of endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia and endometrial cancer risks in pre- and postmenopausal women
[J].
Detection of malignancy in whole slide images of endometrial cancer biopsies using artificial intelligence
[J].
A deep learning model for lymph node metastasis prediction based on digital histopathological images of primary endometrial cancer
[J].
Optimizing ANFIS using simulated annealing algorithm for classification of microarray gene expression cancer data
[J].In the medical field, successful classification of microarray gene expression data is of major importance for cancer diagnosis. However, due to the profusion of genes number, the performance of classifying DNA microarray gene expression data using statistical algorithms is often limited. Recently, there has been an important increase in the studies on the utilization of artificial intelligence methods, for the purpose of classifying large-scale data. In this context, a hybrid approach based on the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), the fuzzy c-means clustering (FCM), and the simulated annealing (SA) algorithm is proposed in this study. The proposed method is applied to classify five different cancer datasets (i.e., lung cancer, central nervous system cancer, brain cancer, endometrial cancer, and prostate cancer). The backpropagation algorithm, hybrid algorithm, genetic algorithm, and the other statistical methods such as Bayesian network, support vector machine, and J48 decision tree are used to compare the proposed approach's performance to other algorithms. The results show that the performance of training FCM-based ANFIS using SA algorithm for classifying all the cancer datasets becomes more successful with the average accuracy rate of 96.28% and the results of the other methods are also satisfactory. The proposed method gives more effective results than the others for classifying DNA microarray cancer gene expression data. Basic structure of proposed method.
Prognostic classification of endometrial cancer using a molecular approach based on a twelve-gene NGS panel
[J].Endometrial Cancer (EC) is one of the most common malignancies in women in developed countries. Molecular characterization of different biotypes may improve clinical management of EC. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project has revealed four prognostic EC subgroups: POLE, MSI; Copy Number Low (CNL) and Copy Number High (CNH). The goal of this study was to develop a method to classify tumors in any of the four EC prognostic groups using affordable molecular techniques. Ninety-six Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples were sequenced following a NGS TruSeq Custom Amplicon low input (Illumina) protocol interrogating a multi-gene panel. MSI analysis was performed by fragment analysis using eight specific microsatellite markers. A Random Forest classification algorithm (RFA), considering NGS results, was developed to stratify EC patients into different prognostic groups. Our approach correctly classifies the EC patients into the four TCGA prognostic biotypes. The RFA assigned the samples to the CNH and CNL groups with an accuracy of 0.9753 (p < 0.001). The prognostic value of these groups was prospectively reproduced on our series both for Disease-Free Survival (p = 0.004) and Overall Survival (p = 0.030).Hence, with the molecular approach herein described, a precise and suitable tool that mimics the prognostic EC subtypes has been solved and validated. Procedure that might be introduced into routine diagnostic practices.
Detection of driver mutations and genomic signatures in endometrial cancers using artificial intelligence algorithms
[J].
Artificial Intelligence Technique for Gene Expression by Tumor RNA-Seq Data: A Novel Optimized Deep Learning Approach
[J].
Producing personalized statin treatment plans to optimize clinical outcomes using big data and machine learning
[J].
Ion Channels and Personalized Medicine in Gynecological Cancers
[J].
Personalized mid-course FDG-PET based adaptive treatment planning for non-small cell lung cancer using machine learning and optimization
[J].
Impact of artificial intelligence on the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of endometrial cancer
[J].
Machine Learning for Endometrial Cancer Prediction and Prognostication
[J].
A deep learning-based automatic staging method for early endometrial cancer on MRI images
[J].
Predicting endometrial cancer subtypes and molecular features from histopathology images using multi-resolution deep learning models
[J].
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Arrhythmia Monitoring
[J].Arrhythmia management has been revolutionized by the ability to monitor the cardiac rhythm in a patient's home environment in real-time using high-fidelity prescription-grade and commercially available wearable electrodes. The vast amount of digitally acquired electrophysiological signals has generated the need for scalable and efficient data processing with actionable output that can be provided directly to clinicians and patients. In this setting, artificial intelligence applications are increasingly important in arrhythmia monitoring, ranging from conventional algorithmic analysis for rhythm determination to more complex deep machine learning methods that have led to the realization of fully automated humanlike rhythm determination in real-time.Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
A Self-Aware Epilepsy Monitoring System for Real-Time Epileptic Seizure Detection
[J].
Convolutional Neural Networks for the Real-Time Monitoring of Vital Signs Based on Impulse Radio Ultrawide-Band Radar during Sleep
[J].